
65
April 2016
All plant parts of wheat and barley samples submitted to the Disease Clinic are
carefully inspected before deciding which pathogens to isolate for, although
both fungi and bacteria are usually targeted to ensure the causal agent is not
overlooked. Plants exhibiting stunted growth, pre-mature discolouration and
incomplete grain fill, are typically infected by root or crown pathogens.
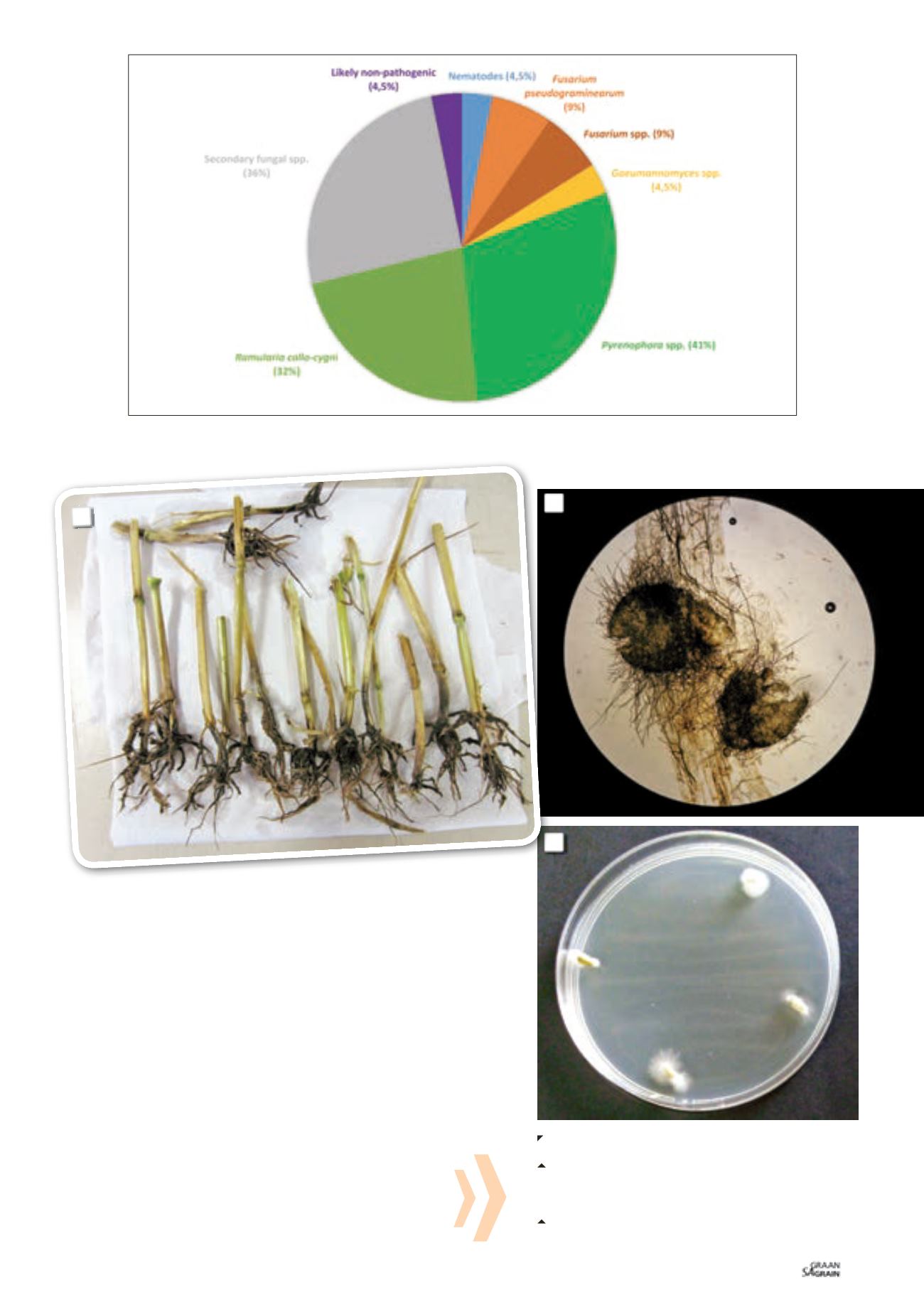
Take-all disease, caused by the fungus
Gaeumannomyces graminis
, is recog-
nised by dark brown to black rotten roots (
Photo 1
). This fungus can be identi-
fied by inspection of the infected tissue under a microscope. Black perithe-
cia, the fruiting bodies carrying fungal spores (
Photo 2
), may be visible on the
crown area, while dark brown ‘runner hyphae’ are often visible on the roots.
When poor root development and/or brown to pinkish discolouration is ob-
served in the crown area of the plant, the infected tissue is surface-sterilised
in 70% ethanol and infected parts plated onto artificial growth media in petri
dishes.
The dishes are incubated at room temperature for three to ten days, to allow
the fungus to grow from the plant tissue onto the media (
Photo 3
). When sev-
eral different fungal colonies emerge on the same dish, the growth is purified
and allowed to grow for an additional three to seven days. The fungal mycelia
can then be used for DNA extraction, if identification based on the visual char-
acteristics of the colony cannot be made.
Graph 2: Pathogenic foliar fungi (in shades of green), root and crown rot fungi (in shades of brown-orange) and other causes
of symptoms identified from 22 barley samples grown in the Western Cape in 2015.
These results are only applicable to the samples submitted to the Disease Clinic
1: Take-all disease, caused by the fungus
Gaeumannomyces
graminis
, recognised by dark brown to black rotten roots.
2: Black perithecia, the fruiting bodies carrying fungal
spores, retrieved from the crown area of wheat infected
with
Gaeumannomyces graminis
, viewed under 400 X
magnification.
3: Fungal growth appearing from surface-sterilised plant
material on artificial media.
2
3
1

















